- Point of view
The next generation of global business services

Global business services (GBS) have evolved. Since COVID-19 forced organizations to invoke business continuity planning (BCP), adapt to virtual working, and push the boundaries of innovation, GBS will not return to the way it was.
Many GBS organizations drive tight collaboration, have hybrid working with data-engagement platforms and other systems of engagement, and continue to adopt digital technologies, though the extent and pace of digital adoption vary.
Forward-looking GBS organizations are at the forefront of adopting technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and blockchain to respond to the changing market dynamics. By embedding predictive and prescriptive analytics, they are creating superior user experiences through insights into their stakeholder community (including customers, suppliers, external parties, firm management, and employees) while also opening continuous-learning opportunities across the organization.
As more GBS organizations drive business growth and become strategic partners, companies will increasingly rely on GBS to expand into additional areas, such as advanced financial planning and analysis and scenario modeling. This will develop and attract top-caliber talent.
The next generation of GBS
What do we mean by GBS?
Global business services are collaborative and efficient organizations that accelerate business outcomes. A GBS is:
- An integral part of end-to-end process execution, which optimizes user experiences
- Focused on enabling digital ways of working that support a virtual workforce and business continuity
- Recognized as an enterprise operating unit that has a seat at the executive leadership table and is the mandated service delivery entity
- A business partner that delivers business insights
- Delivered across the enterprise – globally and at scale – using one or many delivery locations and entities, such as centers of excellence, shared service centers, centers of work, and centers of competencies
- A strategic partner for environmental, social, and governance compliance for business functions in years to come
Why do companies operate global business services?
The importance and role of GBS continue to grow. Organizations are focused on connecting end-to-end processes, reducing cost, driving scale through mergers and acquisitions, accelerating the implementation of new business models, and enabling workforce capabilities, including remote working. Businesses are focusing on developing global business services with a clear purpose: to support the company's strategy by creating value and delivering quality. Of course, value for money and cost management are still key outcomes, but GBS goes beyond a narrow, conventional lens. Key characteristics of future GBS are crystallizing around the following attributes (see figure).
What will drive the next level of global business services (GBS) maturity?
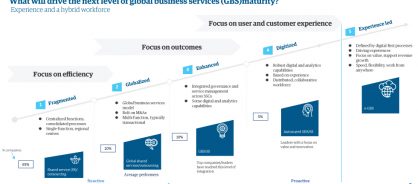
1. Centered on experience, not on functional boundaries
At the heart of successful GBS organizations are their customers and the service they receive. They need to maintain a customer focus throughout the lifecycle of shared service design, build, and operate – by embedding the customer journey into core GBS activities such as continuous improvement and key performance outcomes.
Functional boundaries have long thwarted many efforts to improve productivity and drive benefits. By replacing the traditional model and aligning around experience – or user journeys – to deliver quantitative and qualitative outcomes, GBS will push the boundaries to constantly enhance performance.
For example, a global life sciences company shifted focus away from cost reduction to improved customer satisfaction – especially in placing and fulfilling orders for its products. Another global company reset its shared service center's objectives toward being easy to do business with.
2. Digitally enabled
Automation delivers a step change in efficiency and effectiveness for companies that have standardized and stable processes that are rule-based and repetitive. For example, robotic process automation (RPA) automates routine, repetitive, and rule-based activities.
The next stage in the automation journey beyond RPA is intelligent automation, which includes technologies such as ML and dynamic workflow. Intelligent automation delivers exponential value by learning and adapting as it automates.
Successful future GBS organizations have an ecosystem of partners to ensure they keep ahead of the latest developments and have the range of tools required for automation.
3. Connected by analytics and insights
Tomorrow's GBS leaders are creating dedicated analytics hubs within GBS to continuously mine and use the vast amounts of data flowing through typical operating functions, which creates sustainable augmented intelligence.
By aligning across the process operating towers, GBS can continuously innovate around the specific needs of each unique operating ecosystem and improve time to market by deploying agile analytics development processes. Forward-thinking GBS leaders are using prescriptive and predictive analytics, AI, and cognitive computing to interpret omnistructured data and help make better, faster decisions.
4. Agile to support evolving business strategy
Flexible plug-and-play GBS models help their businesses grow organically and through acquisitions. They either need full integration in the case of carve-outs or partial integration in the case of stand-alone businesses.
GBS models will continue to consistently expand in scope and scale into higher-value areas such as financial planning and analysis, compliance, and integrated operations across finance, sales, IT, HR, and more.
For example, one of the world's largest financial institutions turned to Genpact for help streamlining its compliance efforts and developing smarter overall operations. The business impact has been more than $500 million. The bank has cut its exposure to Regulation E infractions, but more importantly, it has created faster and more efficient onboarding and fund-disbursement processes. These large-scale re-engineering and automation initiatives are delighting customers through exceptional experiences.
5. Reskilling at scale with a distributed workforce
GBS is playing a leading role in underpinning the expectations of an agile workforce.
Thanks to the pandemic, GBS has accelerated digital transformation and given organizations access to the workforce they need – when and where they need it. It has enabled businesses to scale across multiple locations by crafting hybrid working strategies and strengthening BCP across countries. In the future, GBS will be much more flexible while empowering employees with access to the technology and insights they need to work most effectively.
For the workforce, the ability to work remotely or in a hybrid setting means that location is no longer a defining factor. Nurturing and developing talent within a GBS organization is often one of the nonquantifiable benefits in a business case. Higher-value and multifunction services within a GBS provide career paths and development opportunities to keep talent motivated and trained.
For example, a leading global retailer moves top-caliber talent in and out of its GBS center to develop new skills, bringing them back to market roles. This helps promote and develop the GBS center and creates a true partnership with the business. With the introduction of more automation and advanced analytics, the required skills of changing and learning in these areas will be a priority.
6. Custodian of data and standards
GBS will become the nerve center for organizations' wider resources and information, as well as the process-centric and service metrics they operate. For example, there is more scrutiny on data governance, which demands experience in other functions. Companies are being forced to look closely at the quality of their data, its completeness, and possible biases thanks to increasingly complex regulatory requirements, the need for higher data security and privacy, and a greater demand for advanced analytics.
A service framework, which defines how GBS will operate, will be even more important for translating purpose into results. This includes setting out clear key performance indicators (KPIs) and service-level agreements (SLAs) and having a defined and clear service catalog, escalation paths, and effective governance.
7. Led by purpose, focused on innovation
GBS will be the innovation sandbox for adopting digital technologies, not least because of the organization-wide data and insights contained within it. Given the purpose of GBS as far more than a transactional engine, services such as procure to pay and opportunity to cash will run end to end, enabling GBS to impact working capital, reduced revenue leaks, and procurement savings. By aligning GBS objectives to those of the business, high-performing functions become a true strategic business partner with a seat at the top table.
Take a copy for yourself
Aligning around customer experience
Delivering over and above customer expectations has become table stakes. Now, organizations are recognizing that GBS can offer something deeper – experience.
Customer experience is a competitive differentiator that delivers growth, creates impact, and will have a significant influence on the shape of the GBS delivery model. Expected outcomes will match customer needs – this is where GBS plays a critical role. Organizations will follow a disciplined service-management approach, deliver on commitments using agile techniques, and maintain continuous improvement as a core competency, all with customer experience at the core.
GBS centers can play a strategic role for their enterprises. By putting customers first, a high-performing GBS can power the future of shared services. Expanding to provide high-value services and driving improvements through digital and analytics improves the experience for internal stakeholders and delivers benefits beyond cost reduction.
If your GBS organization adopts these seven attributes, it will help harness growth opportunities and take advantage of future business models that are no longer restrained by location.


